Oral health is an essential component of overall well-being, often serving as a window to one’s general health status. Preventive dental care plays a pivotal role in maintaining oral health, mitigating the risk of developing dental diseases, and ensuring a high quality of life. This comprehensive article delves into the significance, methods, and benefits of preventive dental care, underscoring its indispensable role in fostering a healthy society. For optimal results, aligners should be worn for 20-22 hours a day and only removed for eating, drinking anything other than water, and brushing your teeth. and most popular questions answer is Treatment time varies but is usually shorter than traditional braces, averaging 6 to 18 months.
The Significance of Preventive Dental Care
Preventive dental care is the proactive approach to maintaining oral health by averting the onset of dental diseases. It encompasses a range of practices, from regular dental check-ups to daily oral hygiene routines, aimed at preventing dental problems before they arise. This proactive approach is critical, as oral diseases such as dental caries (tooth decay) and periodontal (gum) disease can lead to significant discomfort, pain, and even systemic health problems if left unchecked.
Key Practices in Preventive Dental Care
Regular Dental Check-Ups: Regular visits to the dentist, typically recommended every six months, are the cornerstone of preventive care. These visits allow for the early detection and management of oral health issues, thus preventing their progression. During these check-ups, dentists perform routine examinations, professional cleanings to remove plaque and tartar, and offer personalized advice on maintaining oral health.
Oral Hygiene Education: Knowledge about proper oral hygiene is vital. This includes understanding the correct techniques for brushing and flossing, the importance of using fluoride toothpaste, and recognizing the role of a balanced diet in oral health. Dental professionals play a key role in imparting this knowledge, ensuring individuals are equipped with the right tools and information to maintain their oral health.
Fluoride Use: Fluoride, a naturally occurring mineral, is instrumental in preventing tooth decay. Its application, whether through fluoridated water, toothpaste, mouth rinses, or professional treatments, strengthens the tooth enamel, making it more resistant to acid attacks from bacteria in the mouth.
Dietary Modifications: A balanced diet is essential for oral health. Limiting sugar intake, especially in beverages and snacks, can significantly reduce the risk of cavities. Additionally, a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and dairy products can promote oral health by providing essential nutrients and stimulating saliva production.
Sealants: Dental sealants are a preventive measure especially useful in children and teenagers. These thin, protective coatings are applied to the chewing surfaces of back teeth (molars), preventing food and bacteria from getting trapped in the grooves and crevices of these teeth, thus reducing the risk of decay.
Tobacco Cessation: Avoiding tobacco in all its forms is crucial for oral health. Tobacco use is a major risk factor for gum disease, tooth loss, and oral cancers. Dental clinics can offer guidance and resources for those seeking to quit tobacco use.
Benefits of Preventive Dental Care
The benefits of preventive dental care are multifaceted, impacting not only oral health but overall well-being and quality of life.
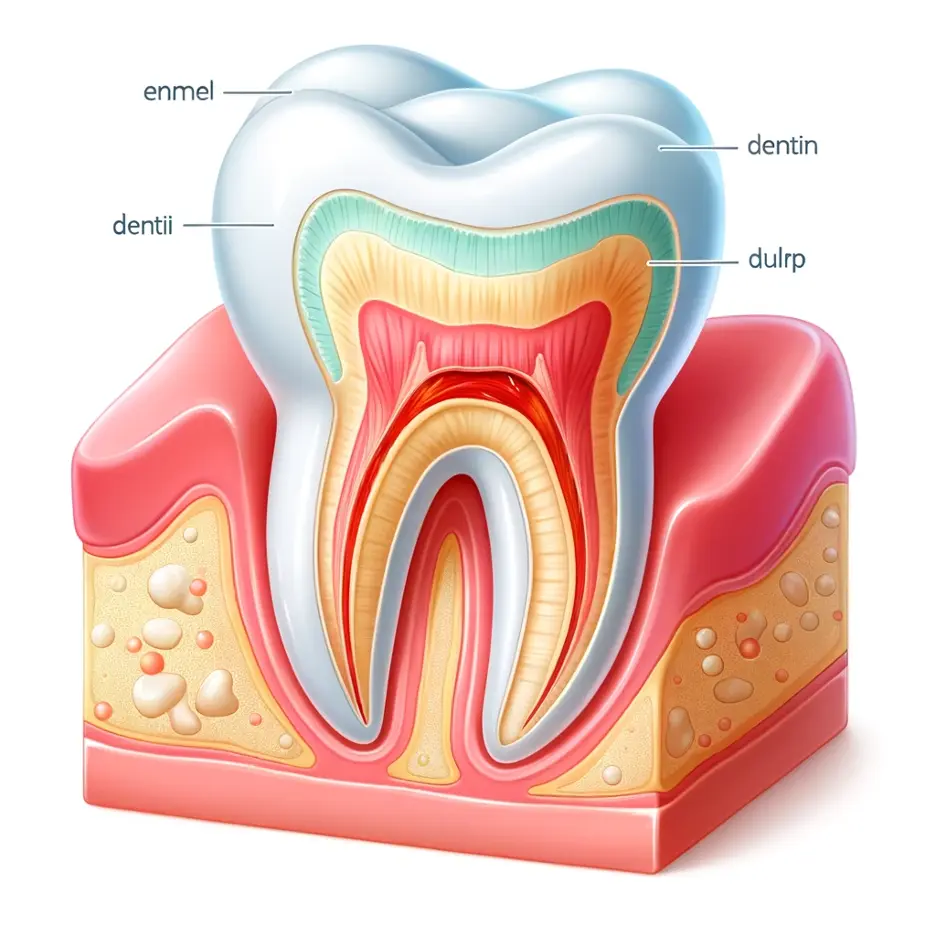
Health Benefits: Preventive care reduces the risk of developing tooth decay, gum disease, and other oral conditions. Early detection and management of these issues can also prevent their progression into more serious health problems, such as heart disease and diabetes, which have been linked to poor oral health.
Economic Benefits: By preventing dental diseases or treating them at an early stage, individuals can avoid the need for more extensive, complex, and expensive dental treatments. This economic efficiency extends to the healthcare system, reducing the burden of dental diseases on public health resources.
Social and Psychological Benefits: Good oral health contributes to a positive self-image and confidence. It enables individuals to eat, speak, and socialize without discomfort or embarrassment, thereby enhancing their quality of life.
Challenges and Future Directions
Despite the clear benefits of preventive dental care, there are challenges to its widespread implementation. Accessibility to dental services, particularly in underserved communities, remains a significant barrier. Additionally, there is a need for greater public awareness and education regarding the importance of preventive oral health practices.
The future of preventive dental care is promising, with advances in technology and research continually enhancing our understanding and methods of care. Innovations such as teledentistry, new diagnostic tools, and tailored preventive strategies based on genetic profiling are on the horizon, promising a more personalized and effective approach to preventive dental care.
Preventive dental care is a fundamental aspect of maintaining oral health and, by extension, overall health and well-being. Its practices, ranging from regular dental check-ups to proper oral hygiene and lifestyle choices, play a crucial role in averting dental diseases and ensuring a high quality of life. While challenges exist, the future of preventive dental care is bright, with ongoing advancements poised to further improve its effectiveness and accessibility. As such, a concerted effort from individuals
